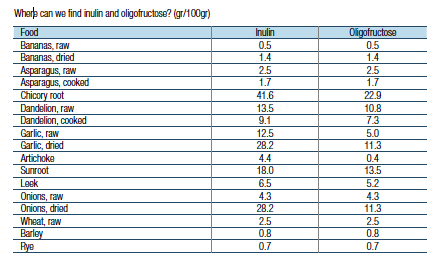
Prebiotics are non-digestible food ingredients, that selectively stimulate growth and/or activity of one or more bacteria in the colon, thus improving the health of the host (Gibson and Roberfroid, 1995). Prebiotics can be defined as non-digestible food ingredients with a positive result on the host because they stimulate metabolic activity of a limited number of micro-organisms such as bifidobacteria and lactobacilli spp. The oligosaccharides are the main components of this group of prebiotics. Components such as inulin and fructooligosaccharides (FOS) form substrates of good bacteria. Inulin and oligofructose consist of linear chains of fructose-molecules with a glucose-molecule as the ending element. Inulin has longer chains than FOS, and is therefore less soluble in cold water than oligofructose, whereby in humid environments it will form a gel. Inulin is also used as a replacement to fat, to avoid overweight and gives no change in taste and texture. Inulin also has a positive effect on the level of cholesterol. Oligofructose is comparable with sucrose, but is less sweet and contains less calories. It is used in food as a substitute for sucrose, because of its abundance of fibres and its low calories. Inulin and oligofructose improve the function of the colon by stimulating the increase of good bacteria. Because of their influence on the intestinal flora, inulin and oligofructose can be classified as probioticum. The good bacteria in the colon can increase by 50% due to the influence of inulin and oligofructose. It is remarkable that the increase in bifidobacteria is not dependant on the amount of inulin intake, but on the number of bifidobacteria in the faeces. The lower this starting quantity, the higher the increase in bifidobacteria.
 Prebiotics are non-digestible food ingredients, that selectively stimulate growth and/or activity of one or more bacteria in the colon, thus improving the health of the host (Gibson and Roberfroid, 1995). Prebiotics can be defined as non-digestible food ingredients with a positive result on the host because they stimulate metabolic activity of a limited number of micro-organisms such as bifidobacteria and lactobacilli spp. The oligosaccharides are the main components of this group of prebiotics. Components such as inulin and fructooligosaccharides (FOS) form substrates of good bacteria. Inulin and oligofructose consist of linear chains of fructose-molecules with a glucose-molecule as the ending element. Inulin has longer chains than FOS, and is therefore less soluble in cold water than oligofructose, whereby in humid environments it will form a gel. Inulin is also used as a replacement to fat, to avoid overweight and gives no change in taste and texture. Inulin also has a positive effect on the level of cholesterol. Oligofructose is comparable with sucrose, but is less sweet and contains less calories. It is used in food as a substitute for sucrose, because of its abundance of fibres and its low calories. Inulin and oligofructose improve the function of the colon by stimulating the increase of good bacteria. Because of their influence on the intestinal flora, inulin and oligofructose can be classified as probioticum. The good bacteria in the colon can increase by 50% due to the influence of inulin and oligofructose. It is remarkable that the increase in bifidobacteria is not dependant on the amount of inulin intake, but on the number of bifidobacteria in the faeces. The lower this starting quantity, the higher the increase in bifidobacteria.
Prebiotics are non-digestible food ingredients, that selectively stimulate growth and/or activity of one or more bacteria in the colon, thus improving the health of the host (Gibson and Roberfroid, 1995). Prebiotics can be defined as non-digestible food ingredients with a positive result on the host because they stimulate metabolic activity of a limited number of micro-organisms such as bifidobacteria and lactobacilli spp. The oligosaccharides are the main components of this group of prebiotics. Components such as inulin and fructooligosaccharides (FOS) form substrates of good bacteria. Inulin and oligofructose consist of linear chains of fructose-molecules with a glucose-molecule as the ending element. Inulin has longer chains than FOS, and is therefore less soluble in cold water than oligofructose, whereby in humid environments it will form a gel. Inulin is also used as a replacement to fat, to avoid overweight and gives no change in taste and texture. Inulin also has a positive effect on the level of cholesterol. Oligofructose is comparable with sucrose, but is less sweet and contains less calories. It is used in food as a substitute for sucrose, because of its abundance of fibres and its low calories. Inulin and oligofructose improve the function of the colon by stimulating the increase of good bacteria. Because of their influence on the intestinal flora, inulin and oligofructose can be classified as probioticum. The good bacteria in the colon can increase by 50% due to the influence of inulin and oligofructose. It is remarkable that the increase in bifidobacteria is not dependant on the amount of inulin intake, but on the number of bifidobacteria in the faeces. The lower this starting quantity, the higher the increase in bifidobacteria.